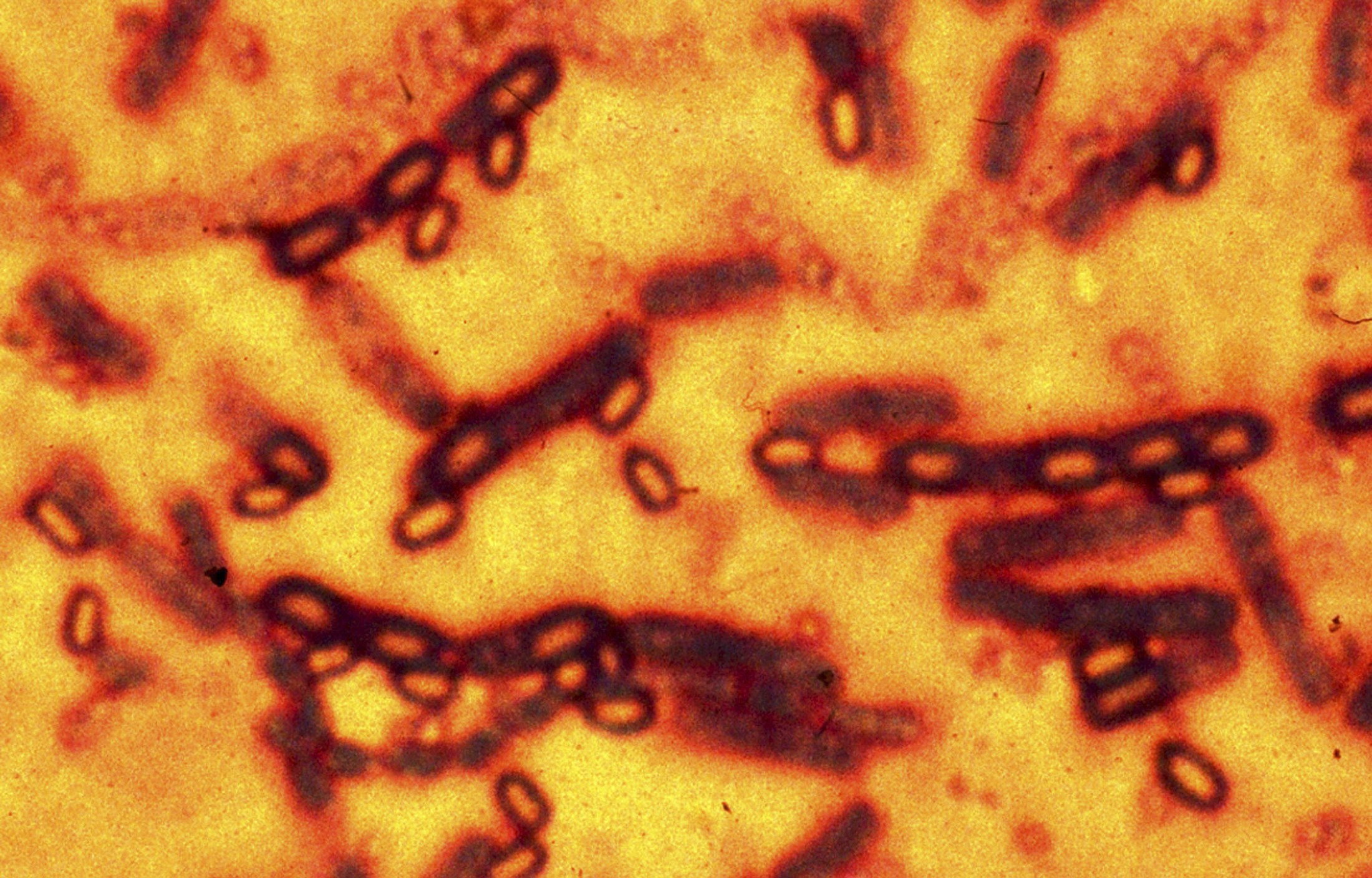
As many as 75 scientists and staff in U.S. government laboratories in Atlanta may have been exposed to live anthrax bacteria after researchers failed to follow safety procedures, prompting an investigation by federal authorities.
Researchers working in a high-security bioterror response lab at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were preparing inactivated samples of the deadly organism, the CDC said on Thursday. But the bacteria may still have been infectious when the samples were transferred to lower-security CDC labs not equipped to handle live anthrax.
Two of the three labs conducted research that may have aerosolized the spores, the CDC said. The agency first detected the exposure on June 13, when live bacteria were found on the original slides used by scientists. Environmental sampling was done and the lab areas remain closed for decontamination.

















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.