If Japanese officials have conducted any clear-eyed, hard-headed analysis of the government's policy options on North Korea's nuclear challenge, they have managed to keep it well hidden.
When India tested a nuclear bomb in 1998 (followed immediately by Pakistan), a range of sanctions were imposed, including by Japan. In the following months I was asked more about that by Japanese shocked by the betrayal of the anti-nuclear cause than anything else about India. Yet in 2005 India was back in good standing as a de facto nuclear-armed state with a special exemption from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (established in reaction to India's 1974 test in the first place) and a bilateral nuclear deal with the United States. By now bilateral deals have been concluded with many other countries, including Australia, Canada and Japan.
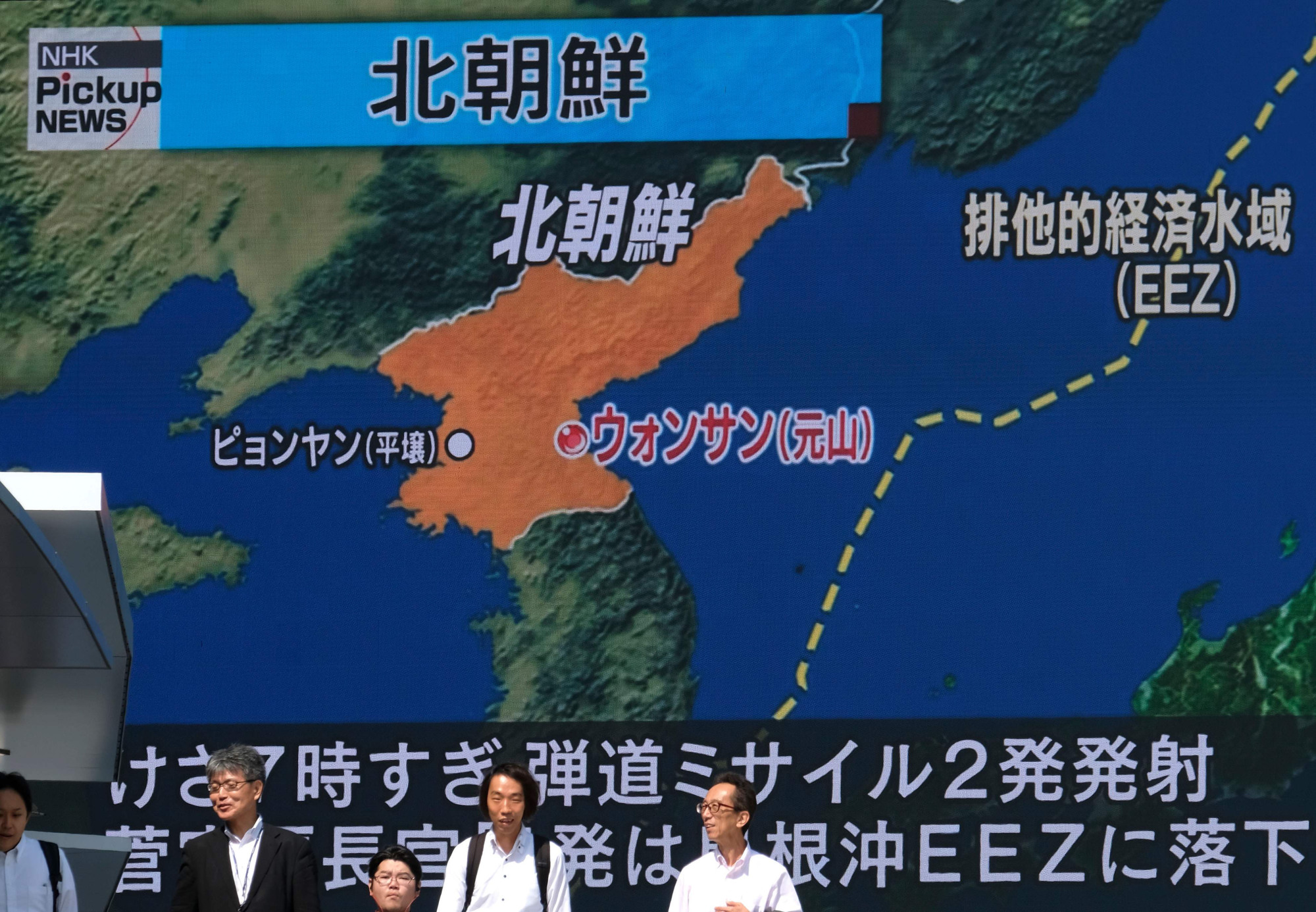
In Lewis Carroll's "Through the Looking Glass," we have this wonderful sentence: "'When I use a word,' Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, 'it means just what I choose it to mean.'" The whistle to signal imminent departure by North Korea's proliferation train was blown in 2003 with its defection from the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. The train left Pyongyang Central in 2006 with North Korea's first nuclear test. The U.S. strategy seems to be to make sure the 2017 sixth test, and no reliable ICBM capability, is the terminus.


















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.