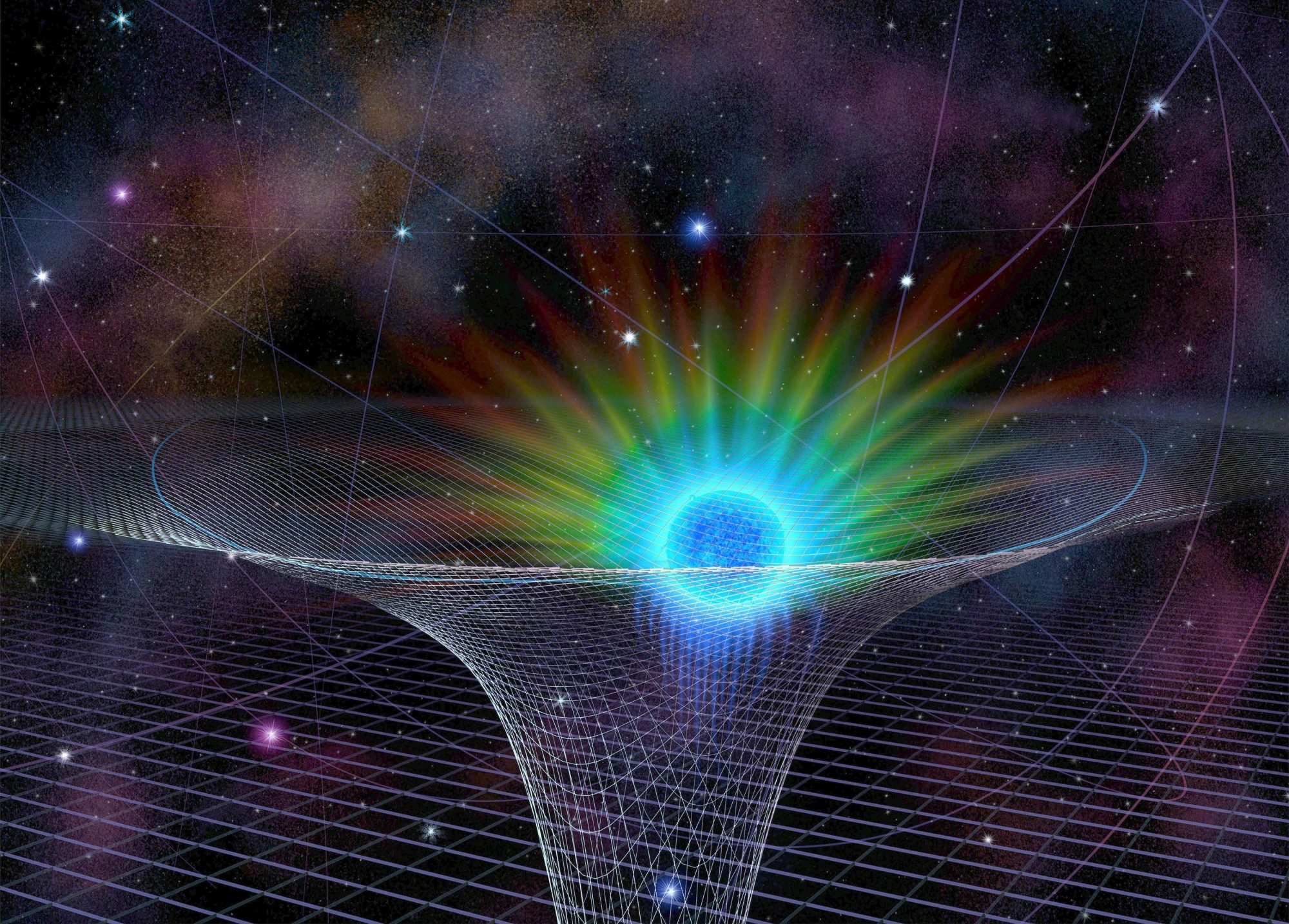
Observations of light coming from a star zipping in orbit around the humongous black hole at the center of our galaxy have provided fresh evidence backing Albert Einstein's 1915 theory of general relativity, astronomers said on Thursday.
Researchers studied a star called S0-2, boasting a mass roughly 10 times larger than the sun, as it travels in an elliptical orbit lasting 16 years around the supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A* residing at the center of the Milky Way 26,000 light-years from Earth.
They found that the behavior of the star's light as it escaped the extreme gravitational pull exerted by the black hole, with 4 million times the sun's mass, conformed to Einstein's theory's predictions. The famed theoretical physicist proposed the theory, considered one of the pillars of science, to explain the laws of gravity and their relation to other natural forces.


















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.