Astronomers have detected the early stages of a colossal cosmic collision, observing a pile-up of 14 galaxies 90 percent of the way across the observable universe in a discovery that upends assumptions about the early history of the cosmos.
Researchers said on Wednesday the galactic mega-merger observed 12.4 billion light-years away from Earth occurred 1.4 billion years after the Big Bang that gave rise to the universe. Astronomers call the object a galactic protocluster, a precursor to the type of enormous galaxy clusters that are the largest-known objects in today's universe.
It marked the first time scientists observed the birth of a galaxy cluster, with at least 14 galaxies crammed into an area only about four times the size of our average-sized Milky Way galaxy.



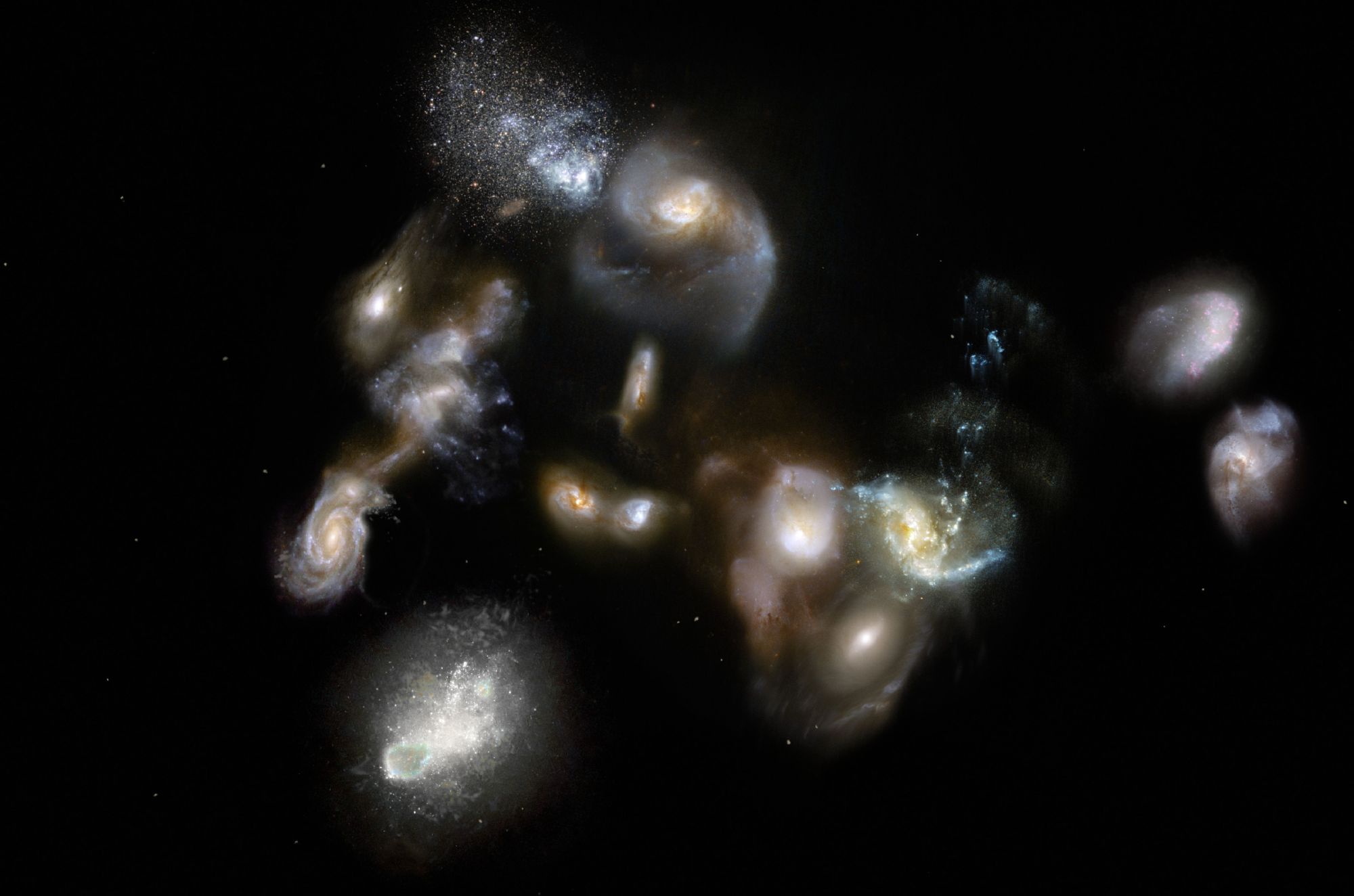















With your current subscription plan you can comment on stories. However, before writing your first comment, please create a display name in the Profile section of your subscriber account page.